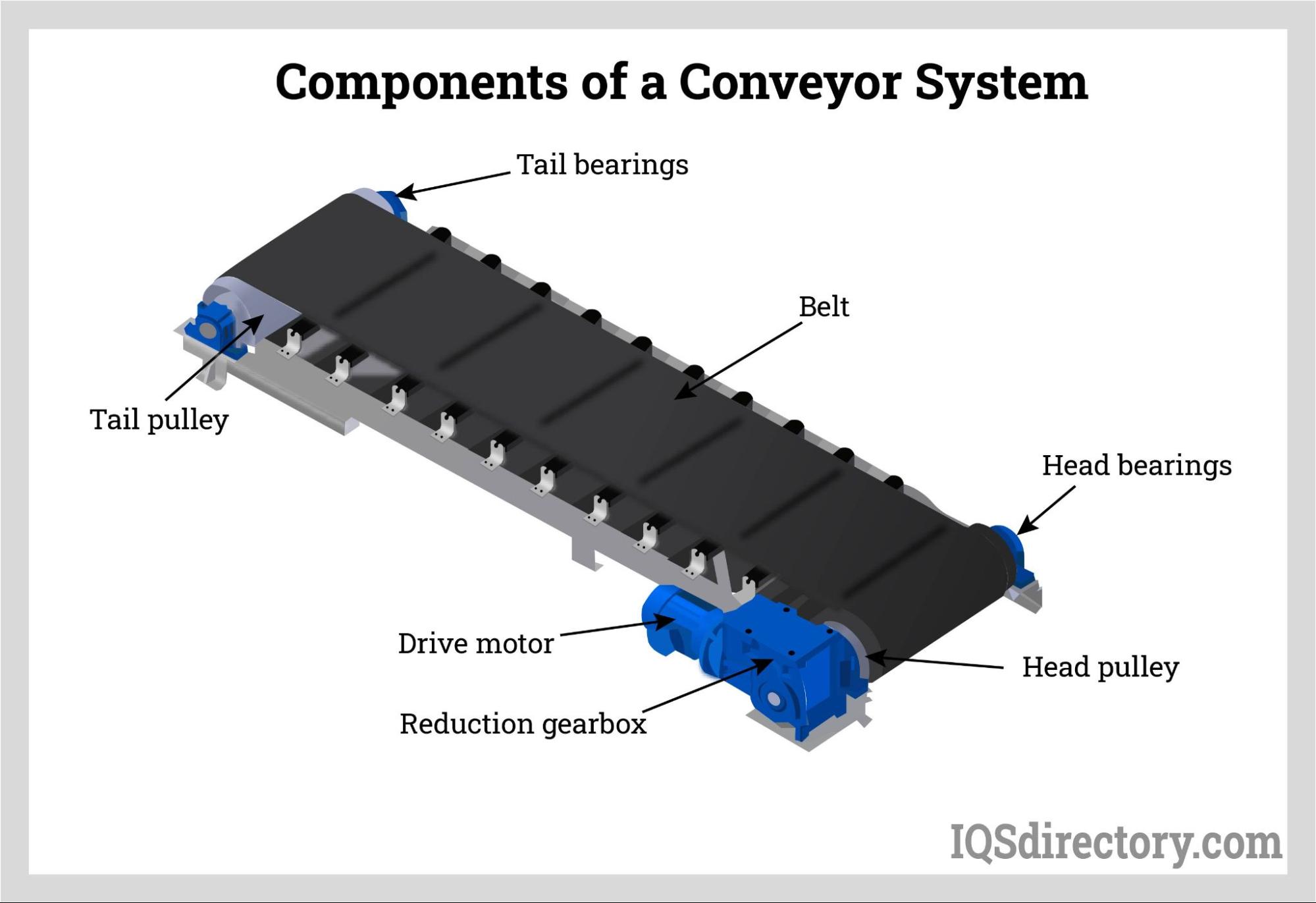
In the article “What Is a Conveyor Belt?” we embark on a journey to understand the fundamental workings of conveyor belts, which are indispensable in various industrial settings and applications. These looped belts are powered by electric motors and are supported by a metal plate bed or rollers. They move materials along a continuously moving path, enhancing productivity, reducing labor costs, and speeding up the transportation of goods for further assembly or storage.
A conveyor belt is driven by pulleys, with the drive pulley powering its movement and an unpowered idler pulley contributing to its support. The location of the pulley drives determines their purpose; head drives are found at the discharge end, while tail drives are situated at the infeed end. Head drives, located at the discharge end, are preferred for their pull force, making them highly efficient for moving conveyor belts.
The versatility of conveyor belts is virtually limitless, with countless types and applications, each serving the common goal of material and goods transportation. While motorized conveyor belts are traditional, some systems rely on non-motorized rollers to move materials, proving that innovation and adaptability are at the core of conveyor technology.
To learn more about May Conveyor products click here
Photo and article with all rights reserved, courtesy of iqsdirectory.com